EmoLabs
Framework and Datasets for CNN Emotion Recognition
Winter 2025/26, Heidelberg
This project started as a Bachelor’s Thesis and was continued beyond.

At the core of this project lies the classification of short speech recordings by emotions. To this end, key technical concepts are related, more than 30 pipelines were implemented, and a well-founded paradigm for competitive architectures derived. In this context, EmoCorpus is introduced, an altered aggregation of widely used emotion-labeled audio datasets. Its counterpart, EmoBench, is distinctly partitioned to enable reproducible evaluations. Pipelines based on Low-Level Descriptors (LLDs) achieved strong performances on low variance data after being augmented with either global attention mechanisms or Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), reaching accuracies of up to 99.5%. Notably, LSTM exhibited the opposite effect for abstract representations (HSFs). These representations, however, attained the highest accuracy on high-variance data (up to 73.5%) once encoder fine-tuning was enabled. The Human Baseline Study (HBS) complemented the SER results by assessing the performance of participants from seven countries on data drawn from EmoCorpus and EmoBench.
Implications in Healthcare
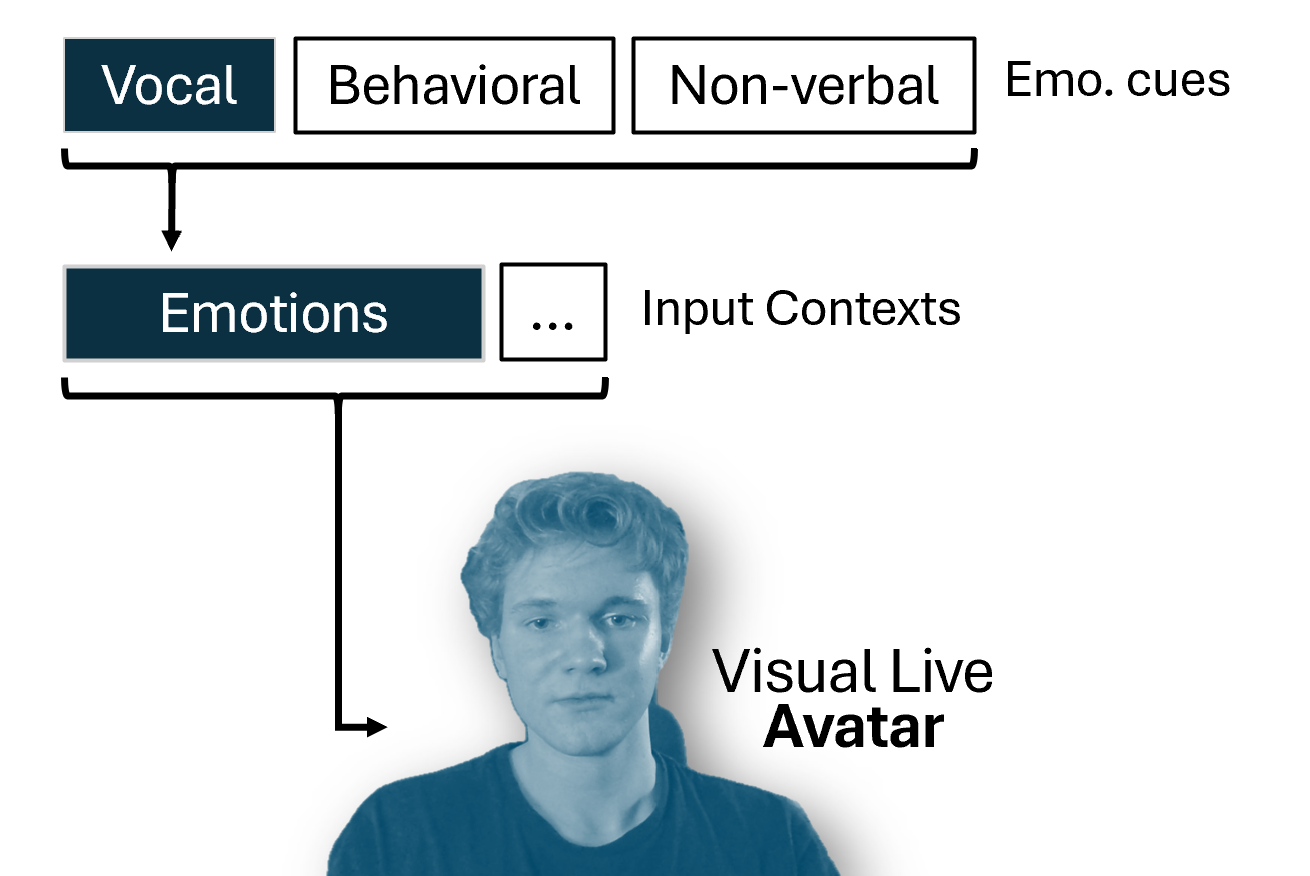
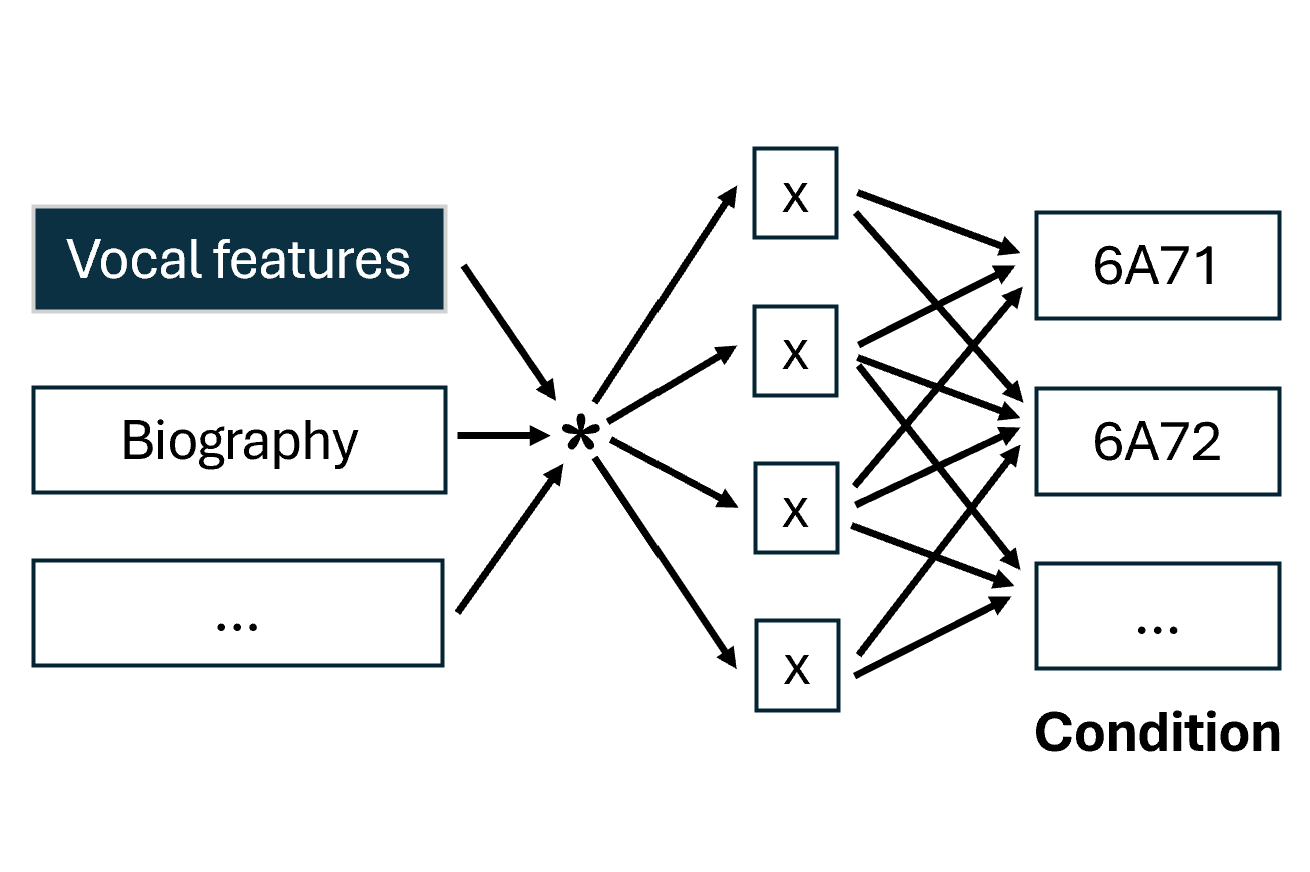
Leveraged Audio Representations
Modular SER-Framework
(1) Sample Standardization
Unify audio input formats, promote consistency.
Algorithmic Procedure:
1. Global Indexing
Scan available datasets, store paths and labels in pairs, along more metadata.
2. Deterministic manifest-split
Generate Base62 on unique project path of each sample. Sort in 9:1 split for training and evaluation by applying mod 10.
3. Waveform normalization
Run standardized algorithm for unifiying channel count, volume coherent to human range of perception and more.
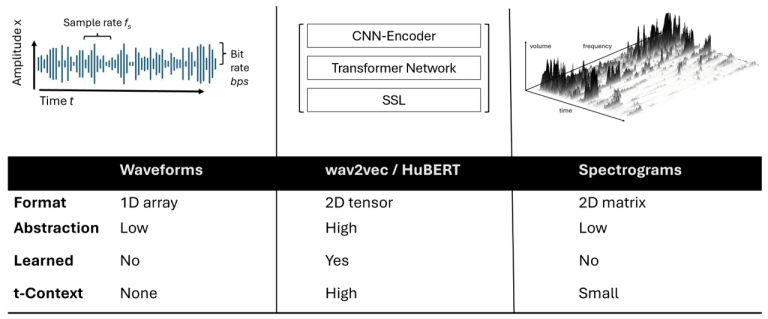
(2) Feature Extraction
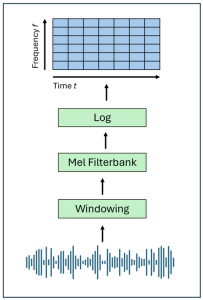
Generate structured pipeline inputs.
Different branches for:
A. Waveforms
Raw signal amplitudes (preserves all initial information; inference for abstraction).
B. wav2vec / HuBERT
Contextualized latent embeddings (with surrounding segments; learned).
C. Spectrograms
Energy distribution across frequency bands.
(3) Convolutional Feature Modeling
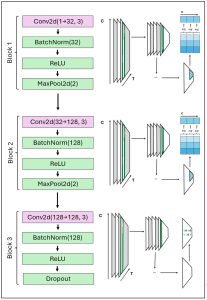
Learn hierarchical patterns from structured inputs.
Different branches for:
1. Classic CNN-Route
3-layer network adjusted for preceding stages and their tensor shapes. Isolated experiments on different network depths and dimensionalities of inputs.
2. ResNet Ablation Study
Addresses the vanishing gradient problem and introdes both increased network depth and residual skip connection. Both are examined in isolated cases.
(4) Temporal Sequence Modeling

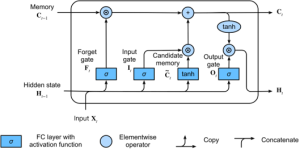
Extend hierarchical patterns by long-term dependencies.
Adresses another bottleneck of classic CNNs: limitation of the temporal scope by the sliding windows.
- Mechanism: Gated memory cells,
- Key idea: control specific rememberance of information across temporal operations,
- Trade-offs: increased capacity, risk of overfitting.
Pipelines examined with and without LSTM.
(5) Feature Aggregation
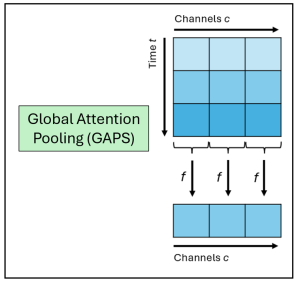
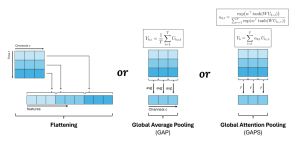
Flatten features into fixed-size representation.
Different branches for:
1. Flattening
Preserve full range of information. Presents elements of non-significant incremental validity to the final fully-connected layer and is likely penalized by lower accuracies.
2. Global Average Pooling
Sum channels by their mean over time.
3. Global Attention Pooling
Sum channels by mean over time, each weighted by importance; rated by the backpropagation feedback machanism.
SER-Datasets
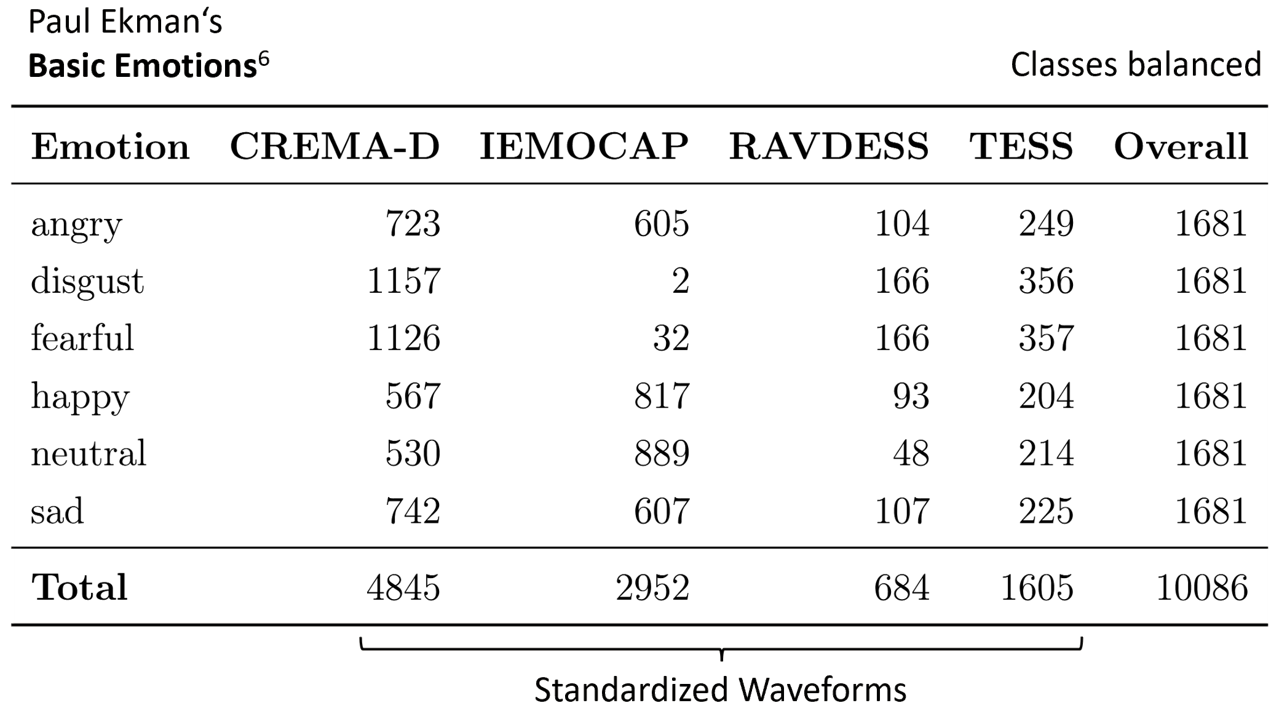
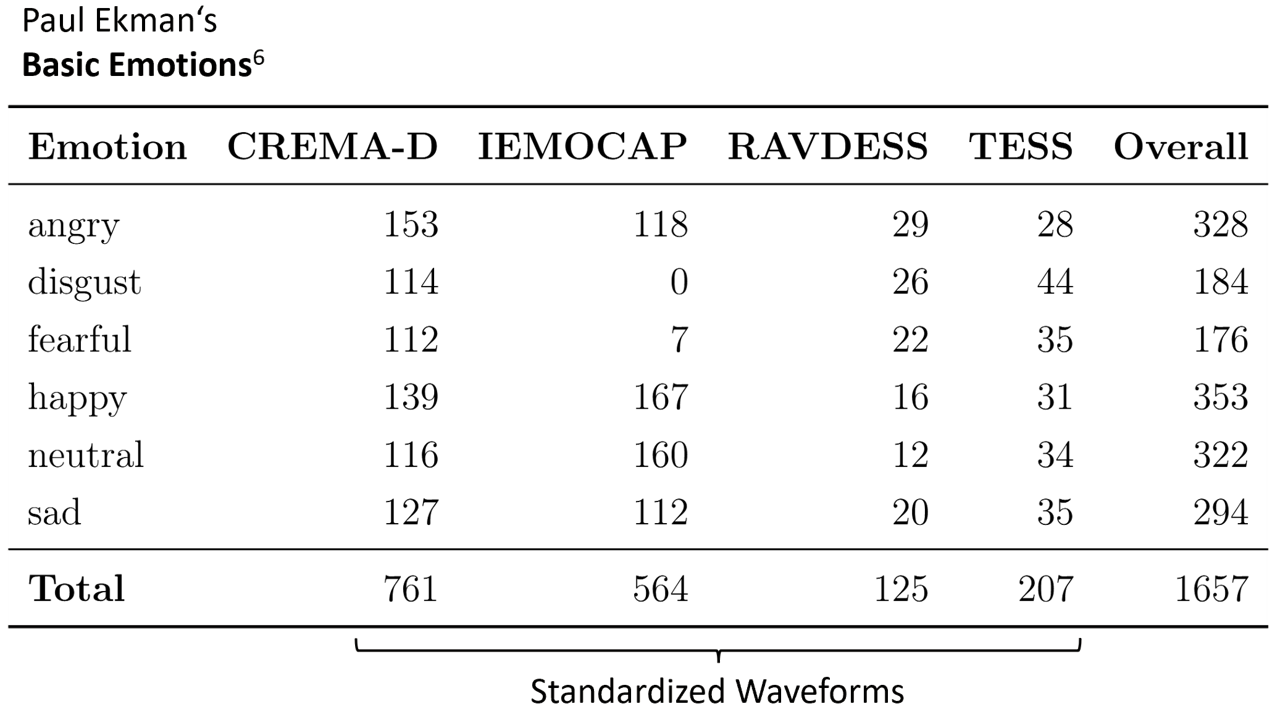
Human Baseline Study
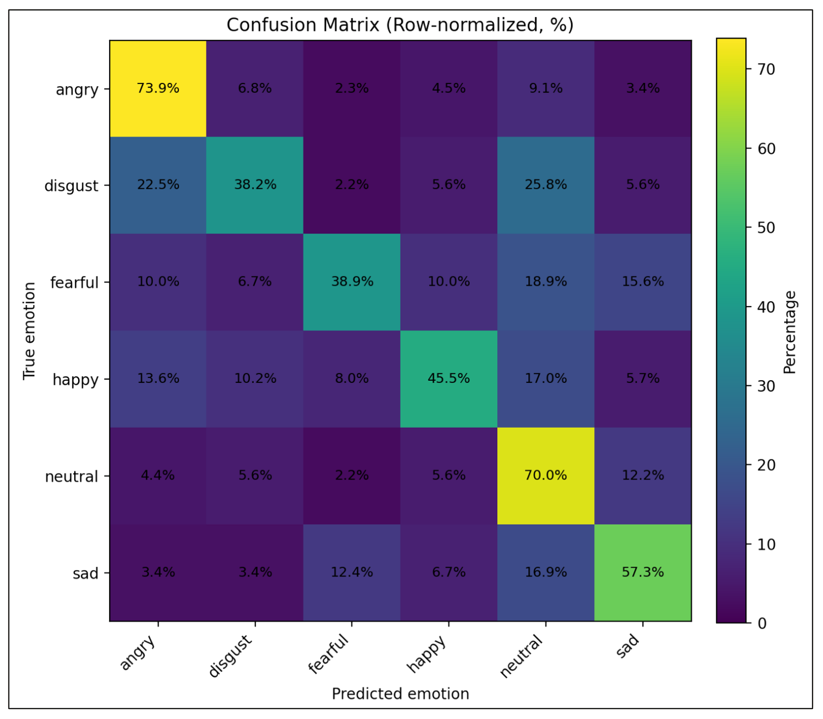
Procedure
1. Participant recruitment
A dozen participants, proficient in English, mixed by gender and background.
2. Randomized sample distribution
60 randomized samples (EmoCorpus, EmoBench), class and source balanced.
3. Meta-analysis of responses
Conversion into unified format; compute recall metrics, trace those back by source.
Statistical Significance
- Constrained by sample size, age distribution; but: aligns with comparable reports.
- Interpreted as approximate anchor point of sample difficulty.
Evaluation of SER-Pipelines
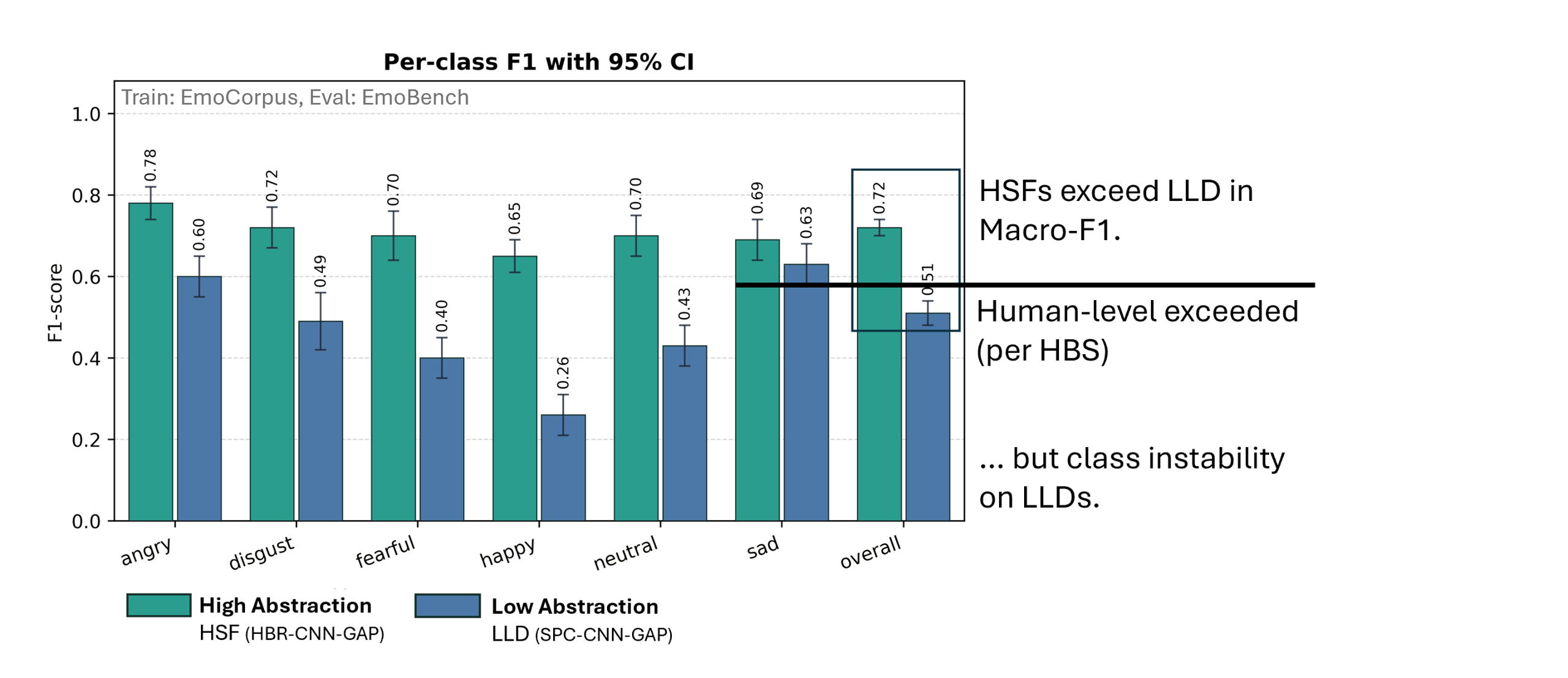
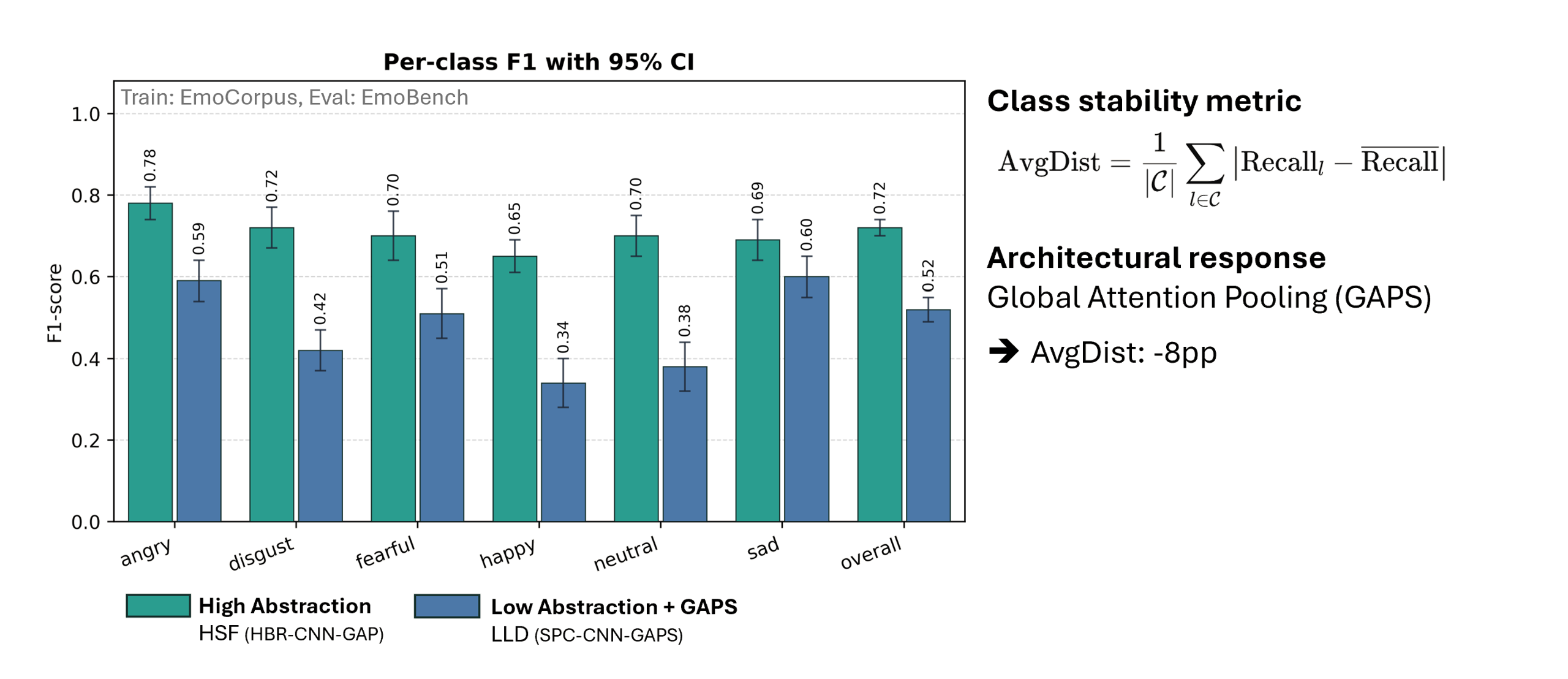
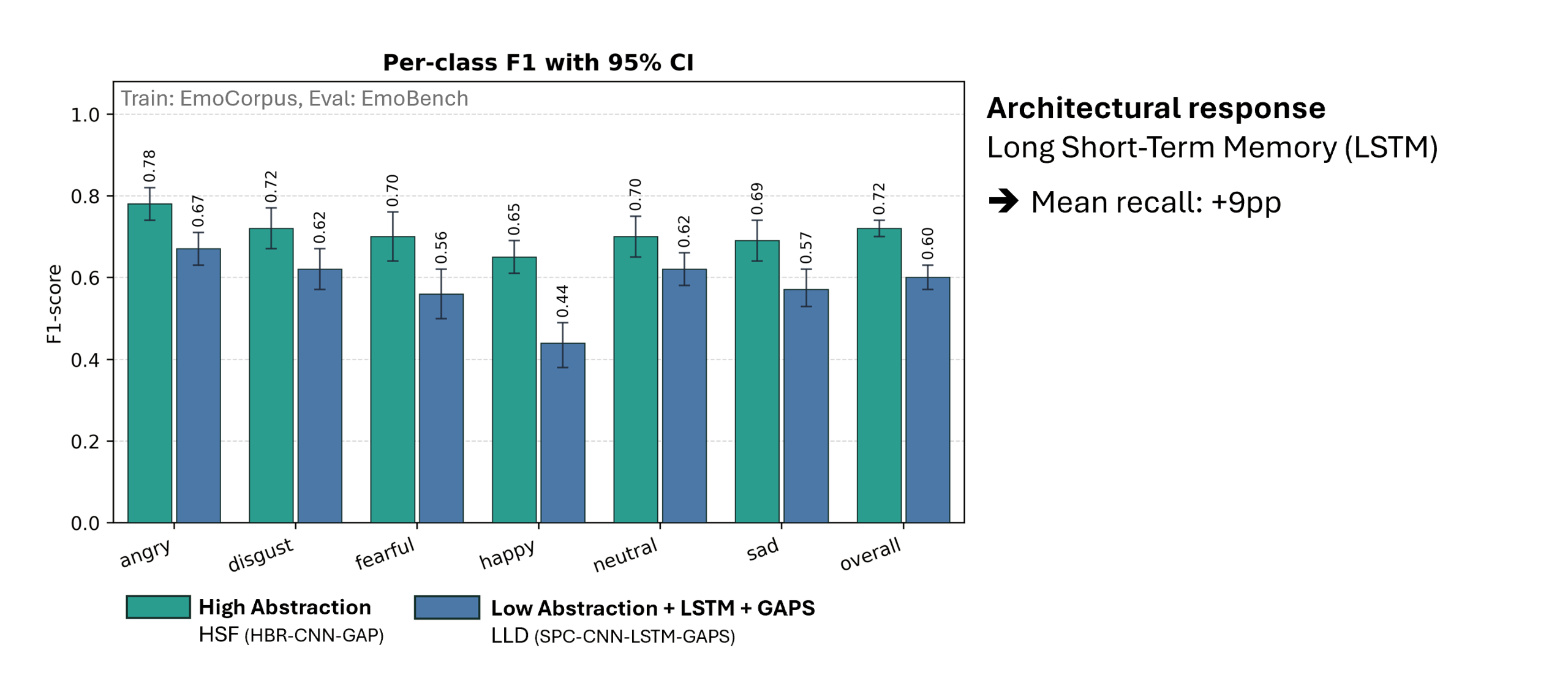
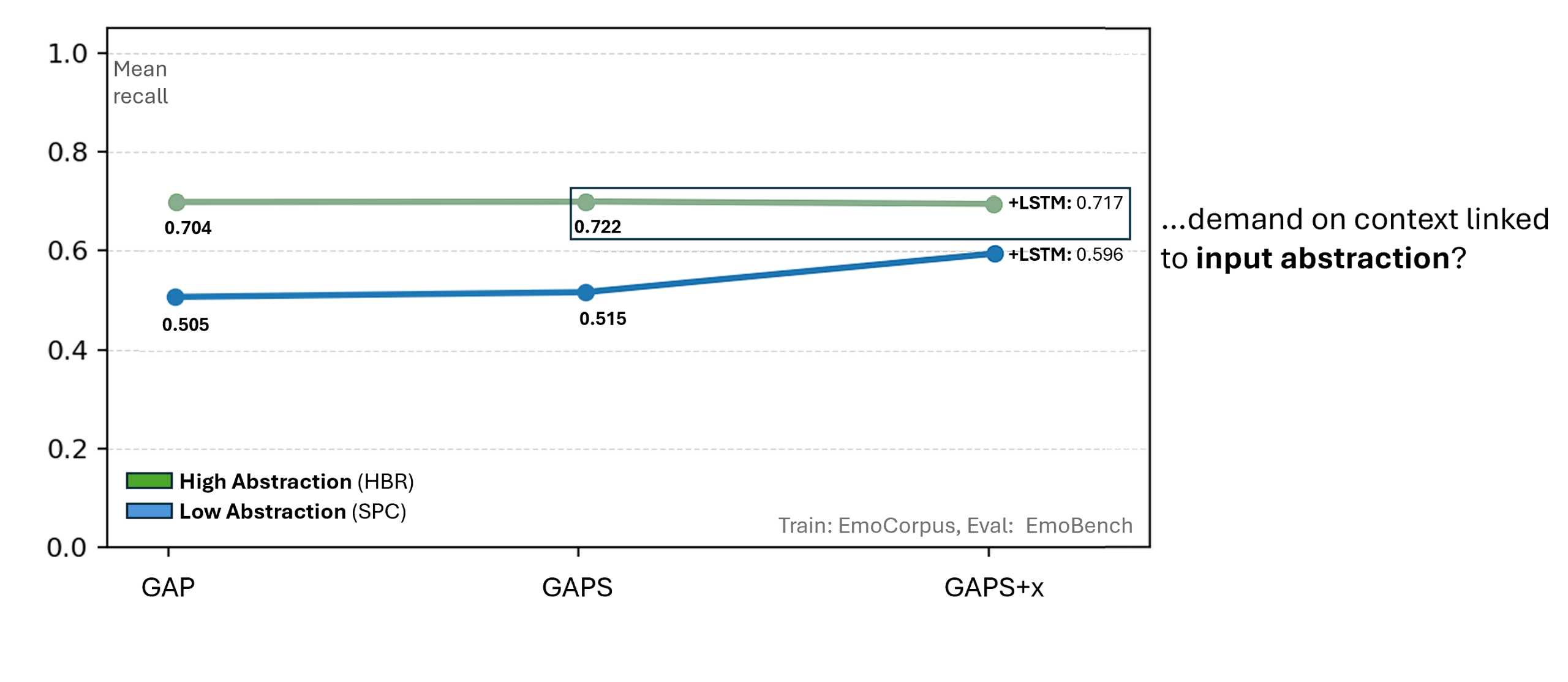
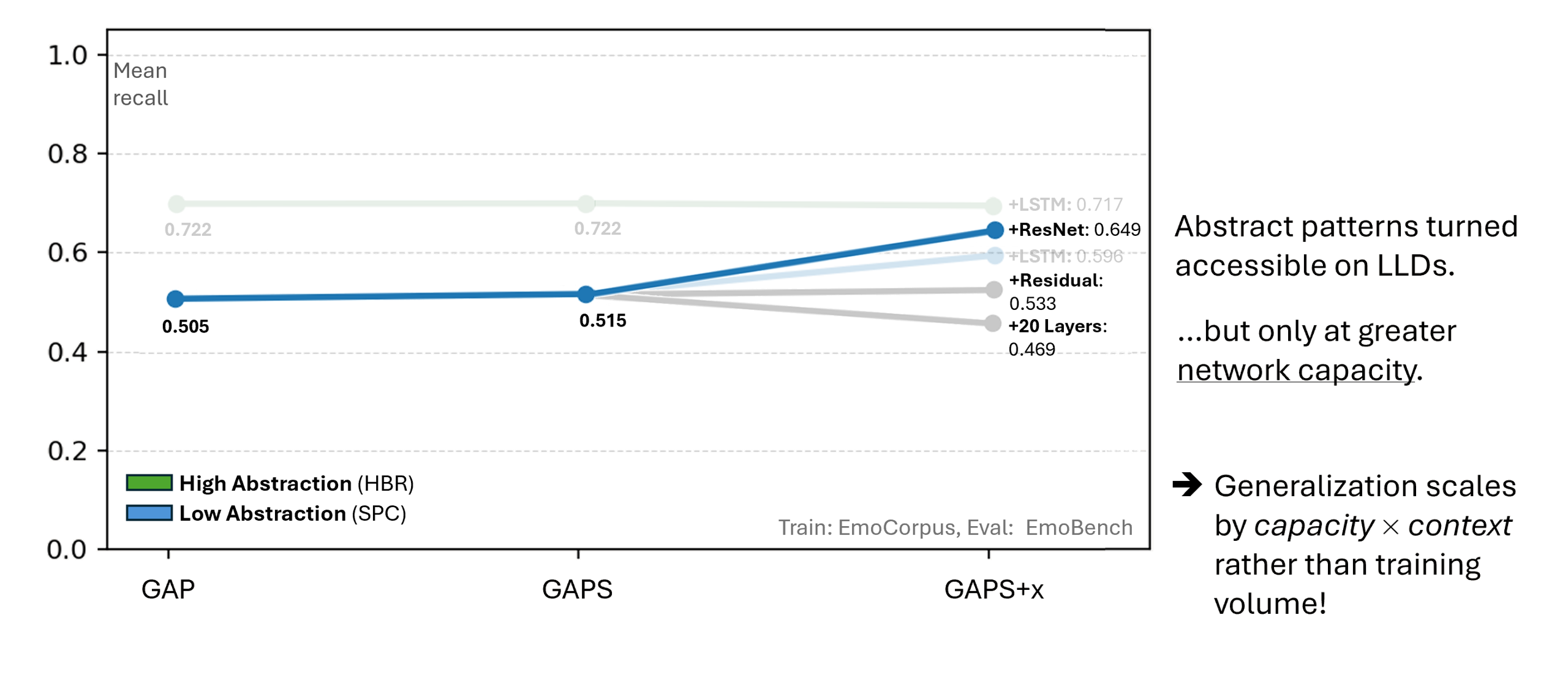
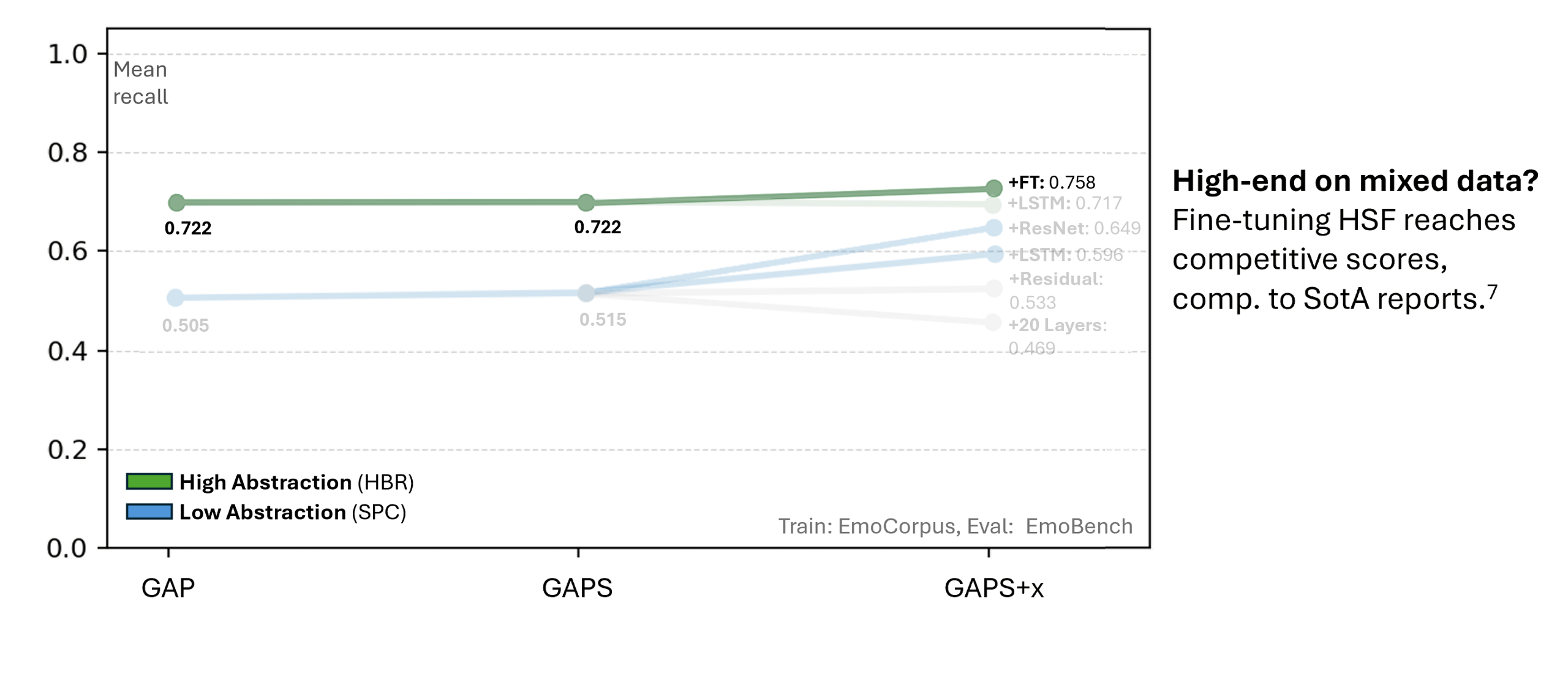
The attached references feature far more evaluations, and most of all according interpretations along key learnings.